In a groundbreaking move set to transform the digital landscape for all, the European Union (EU) has introduced the European Accessibility Act (EAA) 2025.
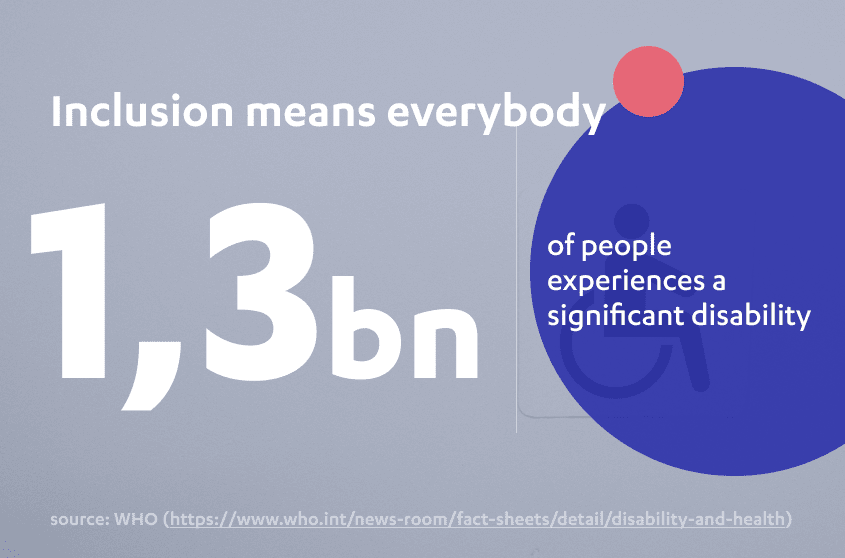
With over 135 million individuals with disabilities across Europe, the need for accessible products and services is crucial as it becomes clear that digital accessibility is no longer an option but a necessity.
July 2024
Why Partnerships Matter
Partnerships play a pivotal role in the success and growth of ecommerce gateways and payments companies. In the fast-paced digital landscape of online commerce, forging strategic alliances can provide a multitude of benefits that extend beyond what a company can achieve on its own.